Inference Pool¶
Alpha since v0.1.0
The InferencePool resource is alpha and may have breaking changes in
future releases of the API.
Background¶
The InferencePool API defines a group of Pods (containers) dedicated to serving AI models. Pods within an InferencePool share the same compute configuration, accelerator type, base language model, and model server. This abstraction simplifies the management of AI model serving resources, providing a centralized point of administrative configuration for Platform Admins.
An InferencePool is expected to be bundled with an Endpoint Picker extension. This extension is responsible for tracking key metrics on each model server (i.e. the KV-cache utilization, queue length of pending requests, active LoRA adapters, etc.) and routing incoming inference requests to the optimal model server replica based on these metrics. An EPP can only be associated with a single InferencePool. The associated InferencePool is specified by the poolName and poolNamespace flags. An HTTPRoute can have multiple backendRefs that reference the same InferencePool and therefore routes to the same EPP. An HTTPRoute can have multiple backendRefs that reference different InferencePools and therefore routes to different EPPs.
Additionally, any Pod that seeks to join an InferencePool would need to support the model server protocol, defined by this project, to ensure the Endpoint Picker has adequate information to intelligently route requests.
How to Configure an InferencePool¶
The full spec of the InferencePool is defined here.
In summary, the InferencePoolSpec consists of 3 major parts:
- The
selectorfield specifies which Pods belong to this pool. The labels in this selector must exactly match the labels applied to your model server Pods. - The
targetPortNumberfield defines the port number that the Inference Gateway should route to on model server Pods that belong to this pool. - The
extensionReffield references the endpoint picker extension (EPP) service that monitors key metrics from model servers within the InferencePool and provides intelligent routing decisions.
Example Configuration¶
Here is an example InferencePool configuration:
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: InferencePool
metadata:
name: vllm-llama3-8b-instruct
spec:
targetPortNumber: 8000
selector:
app: vllm-llama3-8b-instruct
extensionRef:
name: vllm-llama3-8b-instruct-epp
port: 9002
failureMode: FailClose
In this example:
- An InferencePool named
vllm-llama3-8b-instructis created in thedefaultnamespace. - It will select Pods that have the label
app: vllm-llama3-8b-instruct. - Traffic routed to this InferencePool will call out to the EPP service
vllm-llama3-8b-instruct-eppon port9002for making routing decisions. If EPP fails to pick an endpoint, or is not responsive, the request will be dropped. - Traffic routed to this InferencePool will be forwarded to the port
8000on the selected Pods.
Overlap with Service¶
InferencePool has some small overlap with Service, displayed here:
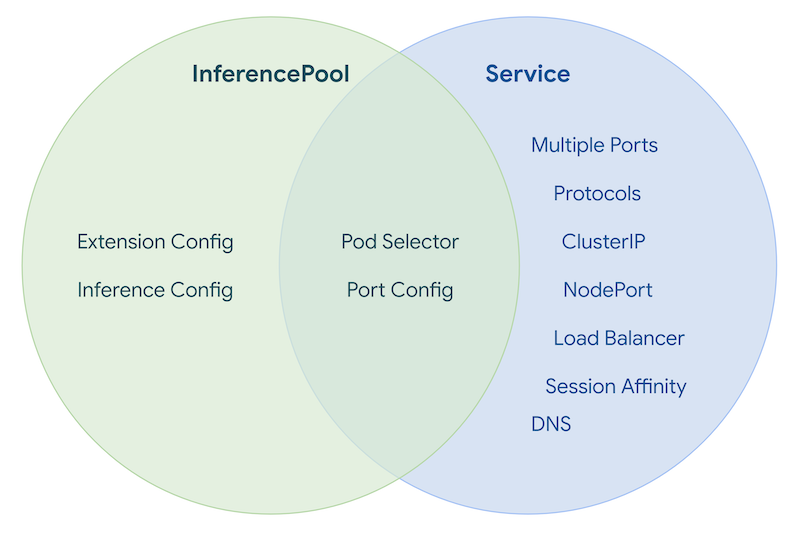
The InferencePool is not intended to be a mask of the Service object. It provides a specialized abstraction tailored for managing and routing traffic to groups of LLM model servers, allowing Platform Admins to focus on pool-level management rather than low-level networking details.
Replacing an InferencePool¶
Please refer to the Replacing an InferencePool guide for details on uses cases and how to replace an InferencePool.